Hydrological properties of Rocks: Comprehensive Guide to Porosity, Specific Yield, and Storage Coefficient in Rocks
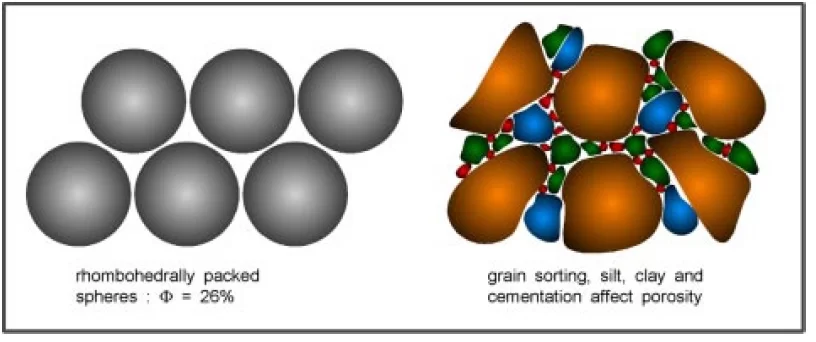
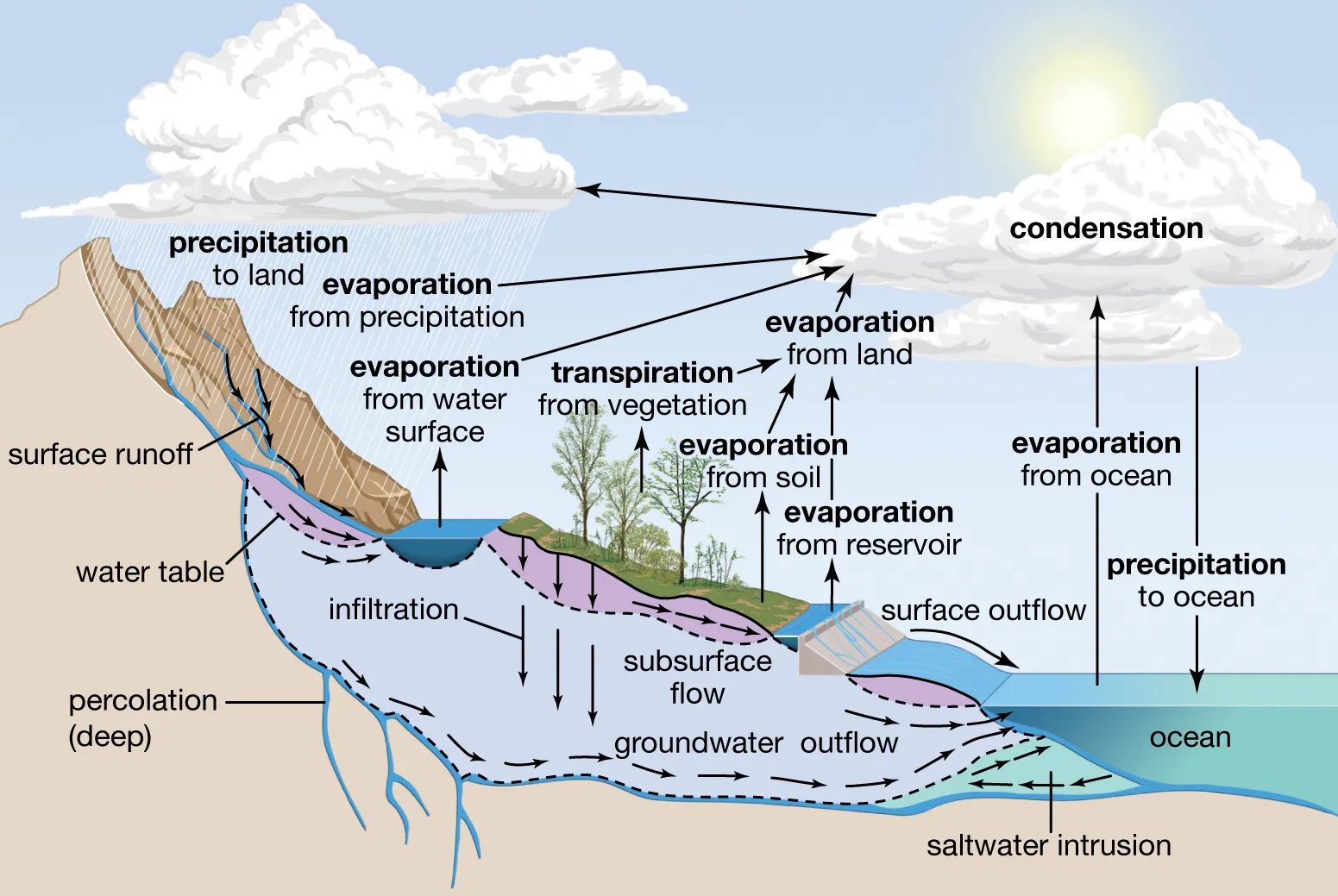
Hydrological properties of Rocks: Hydrological properties are the characteristics of rocks and soils that affect the movement, storage, and distribution of water within the Earth’s crust. These properties include porosity, permeability, specific yield, specific retention,… Hydrological properties of Rocks: Comprehensive Guide to Porosity, Specific Yield, and Storage Coefficient in Rocks