Why is the Arctic heating up twice as fast as the rest of the planet? The answer lies in the surface beneath our feet. This phenomenon, known as the Ice-Albedo Feedback, is a critical climate driver. Unlike simple warming, it acts as a self-perpetuating loop: melting ice exposes dark ocean water, which absorbs more heat, causing even more ice to melt. Understanding this mechanism is key to grasping the urgency of the climate crisis. It explains everything from retreating glaciers to shifting global weather patterns. Dive into the geology and physics behind this powerful feedback loop and what it means for our future.

The Mechanics of the Ice-Albedo Feedback Loop
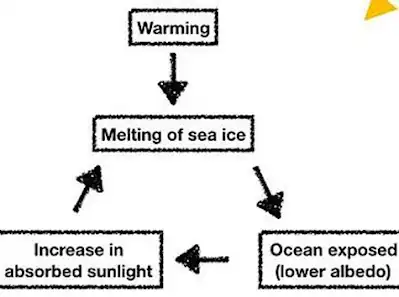
Ice–albedo feedback is a positive (exacerbating) feedback climate process where a change in the area of ice caps, glaciers, and sea ice alters the albedo and surface temperature of Earth. It is prominent in areas where a patch of sea ice completely melts, and results in uncovering darker seawater surface that absorbs more sunlight than ice. Ice reflects some of the solar energy back to space because it is highly reflective. If an equivalent area of ice is replaced by water or land, (having a lower albedo value) reflects less and absorbs more energy, resulting in a warmer Earth.
Recently, it was reported that the Arctic Ocean may become functionally ice-free for part of each year between 2044 and 2067. Further, the Arctic region is heating up twice as fast as the rest of the globe. One reason for this was attributed to ice-albedo feedback mechanism.
Arctic Amplification: How Melting Accelerates Global Warming
Due to increase in temperature, the process results in more melting of ice from underneath, while greenhouse gases in the atmosphere warm the surface resulting in increased humidity. This leads to further melting of ice, which exposes more water to sunlight. Thus, climate change reinforces ice albedo feedback and vice-versa.
Ice-albedo feedback tends to amplify regional warming due to anthropogenic climate change. Due to this amplification, the cryosphere is sometimes called the “natural thermometer” of the earth because changes in each of its components have long lasting effects on biological, physical and social systems on Earth.
There is also potential for increased methane and carbon dioxide release as a result of warming of terrestrial permafrost. Also, with sea ice melting earlier, algae and phytoplankton populations peak earlier and start to decline sooner. For instance, in the Arctic region, crustaceans and fish like the Arctic cod struggle to find enough food and as a consequence impact food chains.
It must be noted that sea ice loss is not just a warning sign of climate change –it is a phenomena that actively drives ecological change. Thus, global efforts must be taken to prevent further melting of sea ice by constantly monitoring sea ice loss and taking adequate measures to prevent human- induced climate change.
Global Consequences: Jet Streams and Weather Extremes
While the ice-albedo feedback loop originates in the polar regions, its destabilizing effects are felt globally. The most critical impact is the disruption of the Polar Jet Stream. As the Arctic warms at a rate faster than the equator (a phenomenon known as Arctic Amplification), the temperature gradient between these two regions weakens.
This reduced temperature contrast causes the jet stream to slow down and become wavier. Instead of a tight, fast-moving river of air, it meanders, locking weather systems in place for extended periods. This “blocking” pattern is directly linked to extreme weather events in the mid-latitudes, including prolonged heatwaves in Europe, stalling hurricanes in North America, and deep freezes in parts of Asia. Understanding the ice-albedo effect is therefore crucial not just for polar geology, but for predicting the frequency of catastrophic weather events worldwide.
FAQs
What is the ice-albedo feedback?
Ice–albedo feedback is a climate process where changes in ice coverage alter the Earth’s albedo, affecting surface temperature. When ice melts, it exposes darker surfaces that absorb more sunlight, causing further warming and accelerating ice loss
What type of climate feedback is the ice-albedo feedback?
The ice-albedo feedback is a positive feedback mechanism, meaning it amplifies climate changes by reinforcing the initial warming effect.
Is ice freezing a positive or negative feedback loop?
Ice freezing is a negative feedback because it increases the Earth’s albedo, reflecting more sunlight and cooling the planet, counteracting warming.
Does ice have a high albedo?
Yes, ice has a high albedo, typically reflecting 50-90% of incoming solar radiation.
What is the albedo of ice and snow?
Fresh snow has an albedo of 0.8 to 0.9 (80-90%), while older ice has a lower albedo around 0.3 to 0.5 (30-50%).
What is a runaway ice-albedo positive feedback?
A runaway ice-albedo feedback occurs when warming causes ice to melt significantly, reducing albedo, increasing absorption of heat, and triggering further melting in an accelerating cycle.
Which surface has the lowest albedo?
The ocean surface has the lowest albedo, around 0.06 (6%), meaning it absorbs most of the sunlight.
Is melting permafrost a positive feedback?
Yes, melting permafrost is a positive feedback, as it releases greenhouse gases like methane (CH₄) and carbon dioxide (CO₂), further warming the atmosphere.
Which color has the highest albedo?
White has the highest albedo because it reflects most of the incoming sunlight.
What is the positive feedback loop of glaciers?
When glaciers melt, they expose darker land or water, absorbing more heat and accelerating further melting, reinforcing the warming effect.
What is the concept of albedo?
Albedo is the measure of a surface’s reflectivity. It ranges from 0 (no reflection, complete absorption) to 1 (total reflection, no absorption).
What is meant by ice-albedo feedback?
It refers to the climate process where melting ice reduces the Earth’s albedo, increasing heat absorption and accelerating further ice loss.
What is positive and negative feedback?
Positive feedback amplifies an initial change (e.g., ice-albedo feedback).
Negative feedback counteracts a change (e.g., cloud formation increasing reflection to cool the planet).
