The Solar System contains 8 official planets as per IAU 2006 definition: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars (terrestrial planets) and Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune (Jovian planets). A planet must orbit the Sun, have sufficient mass for nearly round shape, and clear its orbital neighborhood. Terrestrial planets are rocky with thin atmospheres, while Jovian planets are gas giants with ring systems and numerous moons. Pluto was reclassified as dwarf planet in 2006. Critical topic for UPSC Geography covering astronomy, physical geography, and space science concepts.
What are Planets? Definition and Classification in the Solar System
Planets are solid celestial bodies orbiting the Sun in elliptical orbits. They reflect sunlight but do not emit their own light. Our Solar System includes eight major planets classified as terrestrial (rocky) and Jovian (gaseous) planets, each with unique features and characteristics.
Planets are solid celestial bodies that revolve around a star, such as the Sun, in elliptical orbits. Composed of rock and metal, they do not emit their own light but shine by reflecting sunlight. Unlike stars, planets are closer to Earth and do not twinkle at night. They move from west to east around the Sun, causing their positions to change daily. Planets are much smaller than the Sun or stars. There are eight major planets in our Solar System.
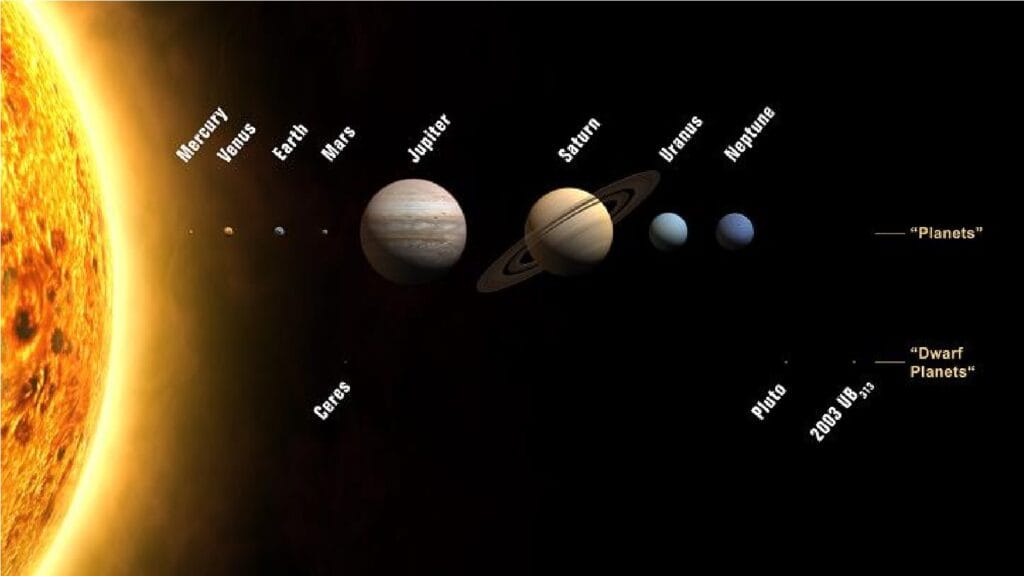
List of Planets in the Solar System (in order of increasing distance from the Sun):
- Mercury (Budha): Nearest to the Sun.
- Venus (Shukra)
- Earth (Prithvi)
- Mars (Mangal)
- Jupiter (Brihaspati): The largest planet.
- Saturn (Shani)
- Uranus (Arun)
- Neptune (Varun)
IAU Official Definition of a Planet
In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) defined a planet in the Solar System as a celestial body that:
- Is in orbit around the Sun,
- Has sufficient mass to assume hydrostatic equilibrium (a nearly round shape),
- Has “cleared the neighborhood” around its orbit, making it the dominant gravitational body in its orbit.
A celestial body that meets the first two criteria but not the third is classified as a dwarf planet. For example, Pluto is considered a dwarf planet because it has not cleared its orbit.
Types of Planets: Terrestrial vs Jovian Classification
Terrestrial Planets
The four planets closest to the Sun—Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars—are known as terrestrial planets due to their Earth-like structure. Common features of terrestrial planets include:
- Thin, rocky crusts
- Mantles rich in iron and magnesium
- Cores of heavy metals
- Thin atmospheres
- Few or no natural satellites
- Varied terrains such as volcanoes, canyons, mountains, and craters
Jovian Planets
The planets beyond Mars—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune—are called Jovian planets, as their structure resembles that of Jupiter. Common features of Jovian planets include:
- Being gaseous bodies
- Possessing ring systems
- Having a large number of natural satellites
Complete Planetary Data and Characteristics
| Sun | MERC URY | VEN US | EAR TH | MO ON | MA RS | JUPIT ER | SATU RN | URAN US | NEPT UNE | PLUT O | |
| Mass (1024k) | 1,988, 500 | 0.33 | 4.87 | 5.97 | 0.07 3 | 0.6 42 | 1898 | 568 | 86.8 | 102 | 0.013 1 |
| Diameter (k m) | 1,392, 684 | 4879 | 12,1 04 | 12,7 56 | 347 5 | 679 2 | 142,9 84 | 120,5 36 | 51,11 8 | 49,52 8 | 2390 |
| Density (kg/ m3) | 1,408 | 5427 | 524 3 | 551 4 | 334 0 | 393 3 | 1326 | 687 | 1271 | 1638 | 1830 |
| Gravity (m/s 2) | 3.7 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 1.6 | 3.7 | 23.1 | 9 | 8.7 | 11 | 0.6 | |
| Escape Velocity (km/ s) | 4.3 | 10.4 | 11.2 | 2.4 | 5 | 59.5 | 35.5 | 21.3 | 23.5 | 1.1 | |
| Rotation Period (hour s) | 1407. 6 | – 583 2.5 | 23.9 | 655. 7 | 24. 6 | 9.9 | 10.7 | -17.2 | 16.1 | – 153.3 | |
| Length of Day (hours) | 4222. 6 | 280 2 | 24 | 708. 7 | 24. 7 | 9.9 | 10.7 | 17.2 | 16.1 | 153.3 | |
| Distance from Sun (106 km) | 57.9 | 108. 2 | 149. 6 | 0.38 4 | 227 .9 | 778.6 | 1433. 5 | 2872. 5 | 4495. 1 | 5870 | |
| Perihelion (1 06 km) | 46 | 107. 5 | 147. 1 | 0.36 3 | 206 .6 | 740.5 | 2741. 3 | 4444. 5 | 4435 | ||
| Aphelion (10 6 km) | 69.8 | 108. 9 | 152. 1 | 0.40 6 | 249 .2 | 1514. 5 | 3003. 6 | 4545. 7 | 7304. 3 | ||
| Orbital Period (days) | 88 | 224. 7 | 365. 2 | 27.3 | 4331 | 10,74 7 | 30,58 9 | 59,80 0 | 90,58 8 | ||
| Orbital Velocity (km/ s) | 47.9 | 35 | 29.8 | 1 | 24. 1 | 13.1 | 9.7 | 6.8 | 5.4 | 4.7 | |
| Orbital Inclination (d egrees) | 7 | 3.4 | 0 | 5.1 | 1.9 | 1.3 | 2.5 | 0.8 | 1.8 | 17.2 | |
| Orbital Eccentricity | 0.205 | 0.00 7 | 0.01 7 | 0.05 5 | 0.0 94 | 0.049 | 0.057 | 0.046 | 0.011 | 0.244 | |
| Axial Tilt (degrees) | 0.01 | 177. 4 | 23.4 | 6.7 | 25. 2 | 3.1 | 26.7 | 97.8 | 28.3 | 122.5 | |
| Mean Temperature (C) | 167 | 464 | 15 | -20 | -65 | -110 | -140 | -195 | -200 | -225 | |
| Surface Pressure (bar s) | 0 | 92 | 1 | 0 | 0.0 1 | Unkn own | Unkn own | Unkn own | Unkn own | 0 | |
| Number of Moons | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 67 | 62 | 27 | 14 | 5 | |
| Ring System? | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | |
| Global Magnetic Field? | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unkn own |
Solar System Planets – Key Facts for UPSC/SSC/PSC Exams
- Total Planets: 8 (official IAU definition since 2006)
- Terrestrial Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars (inner planets)
- Jovian Planets: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune (outer planets)
- Largest Planet: Jupiter (more massive than all other planets combined)
- Smallest Planet: Mercury (smaller than Jupiter’s moon Ganymede)
- Hottest Planet: Venus (464°C due to greenhouse effect)
- Coldest Planet: Neptune (-200°C average temperature)
- Only Life-Supporting Planet: Earth (habitable zone, liquid water)
- Dwarf Planets: Pluto, Eris, Ceres, Haumea, Makemake
- Asteroid Belt: Between Mars and Jupiter orbits
FAQs
What are the planets and their classification?
Planets are classified into two main types:
Terrestrial Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These are rocky planets with solid surfaces.
Jovian Planets (Gas Giants): Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These planets are composed mostly of gas and have ring systems.
What are the 8 planets and their definition?
The eight planets in the Solar System are:
Mercury: The smallest and closest to the Sun.
Venus: Known as Earth’s twin due to its similar size.
Earth: The only planet known to support life.
Mars: The “Red Planet” with a thin atmosphere.
Jupiter: The largest planet, mainly composed of gas.
Saturn: Famous for its ring system.
Uranus: A gas giant that rotates on its side.
Neptune: The farthest planet with strong winds and storms.
What is the definition of the Solar System and planets?
The Solar System consists of the Sun and all celestial bodies bound to it by gravity, including planets, moons, asteroids, and comets.
A planet is a celestial body that orbits the Sun, has enough mass to form a nearly round shape, and has cleared its orbit of other debris.
What are the 9 planets and their characteristics?
Earlier, Pluto was considered the ninth planet, but it was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006. The nine planets (before reclassification) and their characteristics are:
Mercury: Small, rocky, closest to the Sun.
Venus: Thick atmosphere, extremely hot.
Earth: Supports life, has liquid water.
Mars: Red surface, thin atmosphere.
Jupiter: Largest, has a Great Red Spot.
Saturn: Rings made of ice and dust.
Uranus: Rotates sideways.
Neptune: Strongest winds.
Pluto (Dwarf Planet): Ice-covered, eccentric orbit.Earlier, Pluto was considered the ninth planet, but it was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006. The nine planets (before reclassification) and their characteristics are:
Mercury: Small, rocky, closest to the Sun.
Venus: Thick atmosphere, extremely hot.
Earth: Supports life, has liquid water.
Mars: Red surface, thin atmosphere.
Jupiter: Largest, has a Great Red Spot.
Saturn: Rings made of ice and dust.
Uranus: Rotates sideways.
Neptune: Strongest winds.
Pluto (Dwarf Planet): Ice-covered, eccentric orbit.
What is the definition of a planet?
A planet is a celestial body that:
Orbits the Sun.
Has sufficient mass to form a nearly round shape.
Has cleared its orbit of other debris.
What are the five characteristics of planets?
Must orbit the Sun.
Must have enough gravity to form a nearly round shape.
Must have cleared its orbital path.
Must have a stable orbit.
May have moons or rings.
What is the Solar System short note?
The Solar System consists of the Sun, eight planets, their moons, asteroids, and comets. The planets orbit the Sun in elliptical paths due to gravity. It was formed about 4.6 billion years ago.
Which is the hottest planet?
Venus is the hottest planet, with an average surface temperature of about 464°C due to its thick atmosphere trapping heat.
What are the 12 planets and their definition?
There are officially 8 planets, but some proposals include:
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto (Dwarf Planet)
Eris (Dwarf Planet)
Ceres (Dwarf Planet)
Haumea (Dwarf Planet)
Who defined the Solar System?
The concept of the Solar System was developed over centuries. Nicolaus Copernicus (1543) proposed the heliocentric model, where planets revolve around the Sun.
Why is Earth called the blue planet?
Earth is called the Blue Planet because 71% of its surface is covered in water, making it appear blue from space.
What are the classifications of planets?
Planets are classified into:
Terrestrial Planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars.
Jovian (Gas Giants): Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune.
Dwarf Planets: Pluto, Eris, Ceres.
What color is Mercury?
Mercury appears grayish due to its rocky surface.
For latest planetary data and space missions, visit NASA Solar System Exploration.
Official IAU planet definitions and classifications at International Astronomical Union.
Real-time planetary positions and data from NASA JPL Solar System Dynamics.
For UPSC preparation, refer to NCERT official geography textbooks.
Space science education resources at European Space Agency Education.
