How Much Melatonin to Take
What is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a naturally occurring hormone synthesized by the body to regulate the circadian rhythm, specifically the sleep-wake cycle. As evening approaches and ambient light diminishes, the production of melatonin increases, sending crucial biological signals that it is time to initiate rest and prepare for sleep. Consequently, melatonin supplementation has gained significant traction among individuals experiencing insomnia, jet lag, delayed sleep phase disorder, or other fundamental disturbances to their internal biological clock.
Nevertheless, the growing reliance on melatonin supplements has given rise to concerns about inappropriate dosages and the potential risks of excessive intake. Acquiring a comprehensive understanding of melatonin’s essential physiological function, the regulatory framework governing supplement production, and the appropriate dosage guidelines is vital for ensuring its safe and effective use.
How Much Melatonin Should You Take?
Although no officially established dosage for melatonin exists, the majority of individuals utilizing it as a sleep aid typically consume between 1 to 5 milligrams approximately 30 minutes prior to their intended bedtime. Commercially available melatonin formulations vary considerably in potency, with available doses spanning from 200 micrograms up to 20 milligrams, and are accessible in multiple distinct delivery formats, including:
- Tablets
- Capsules
- Gummies
- Liquid drops
- Melts or lozenges
- Patches
- Sprays
Melatonin Dosage for Adults
Specialists advise initiating melatonin supplementation with a low dosage, generally around 0.5 to 1 milligram, administered 30 to 60 minutes prior to sleep. Beginning with a minimal dose enables individuals to assess their physiological response while minimizing the likelihood of experiencing adverse effects, such as grogginess or intensified dreams. If necessary, the amount may be incrementally increased in 1-milligram intervals; however, most adults report that effective results for addressing sleep-related issues like insomnia or jet lag are typically achieved within the 1 to 3 milligram range.
The optimal dosage of melatonin differs among individuals, as various factors—including age, body mass, melatonin sensitivity, pre-existing medical conditions, and the intended purpose of supplementation—can all influence the body’s response. As with any nutritional supplement, it is essential to consult a qualified healthcare provider before initiating melatonin use, particularly for individuals who are concurrently taking prescription medications or managing chronic health disorders.
Melatonin Dosage for Older Adults
Individuals over the age of 65 are advised to seek medical consultation before beginning melatonin supplementation. Research involving this demographic remains limited, and the use of melatonin may pose additional health risks in older adults.
Healthcare professionals recommend that older individuals adopt the lowest effective dose for a brief duration, rather than engaging in long-term usage, to minimize potential adverse effects and ensure safe administration.
Melatonin Dose for Kids
Although melatonin supplements may be considered safe for children in certain cases, comprehensive clinical research in pediatric populations remains limited. Therefore, it is crucial for parents and caregivers to consult a medical professional before administering melatonin to minors.
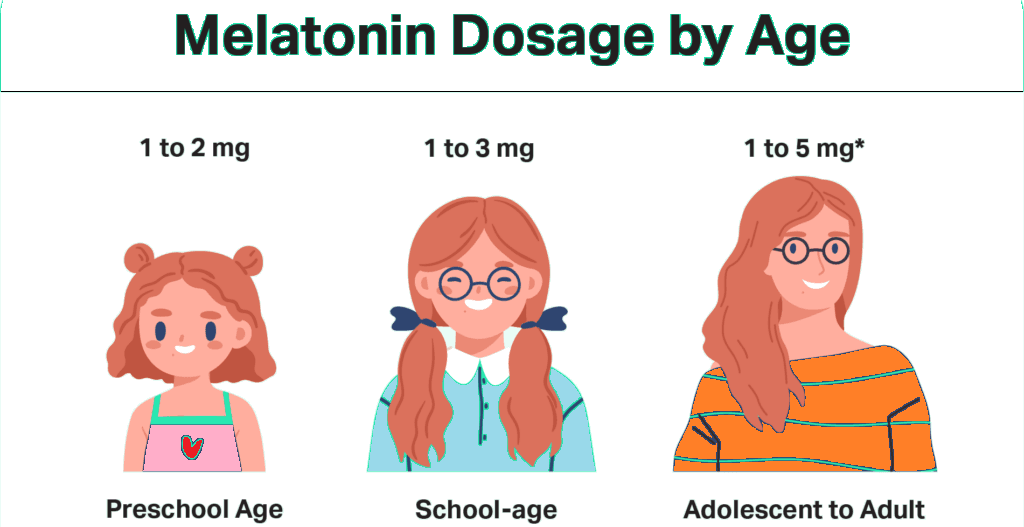
When used to address pediatric insomnia, melatonin dosage is typically determined by the child’s developmental stage. Preschool-aged children are generally prescribed 1 to 2 milligrams, school-aged children often receive 1 to 3 milligrams, and adolescents may be given 1 to 5 milligrams, depending on individual clinical needs.
Prior to considering melatonin, parents and caregivers are encouraged to explore alternative behavioral strategies for enhancing sleep hygiene. These include minimizing screen time during evening hours, maintaining a comfortable room temperature, establishing a regular bedtime schedule, and implementing a consistent nightly routine to support natural sleep onset.
