Buddhism: Origins, Philosophy, and Traditions
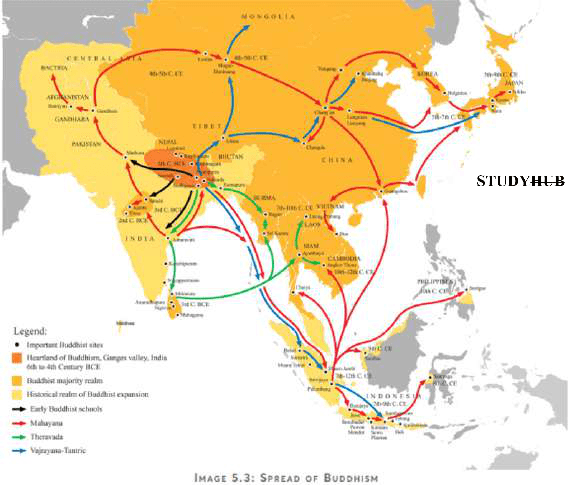
Buddhism, originating in ancient India around the 6th-5th century BCE with Siddhartha Gautama (the Buddha), is a philosophy and religion focused on overcoming suffering (dukkha) by understanding its causes, following ethical principles, and attaining enlightenment (nirvana) through practices like meditation, leading to major traditions such as Theravada and Mahayana, and profoundly influencing Asian culture. Its core tenets involve the Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path, emphasizing non-violence, compassion, and escaping the cycle of rebirth (samsara).