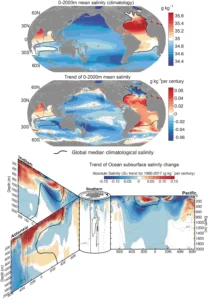
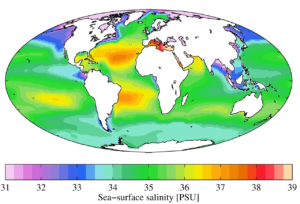
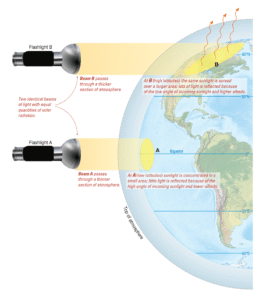
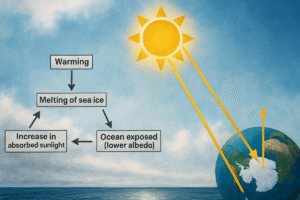
Ocean salinity variations result from five primary physical processes that work simultaneously across global marine systems. Evaporation increases salinity by removing pure water while leaving...
Read Moreoceanography
studyhub.net.in
Salinity of Ocean Water
As an oceanographer who has spent decades sampling the vast waters of our planet, from the frigid poles to the […]
Read MoreHow does latitude affect solar radiation?
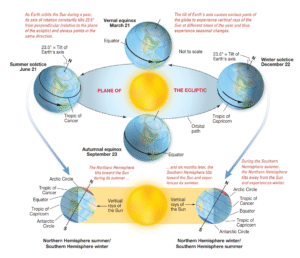
How Latitude Affects the Distribution of Solar Radiation If Earth were a flat surface oriented perpendicularly to the Sun, solar […]
Read MoreWhat is the ocean heating phenomenon? Complete Guide
Ocean heating phenomenon refers to the systematic redistribution of thermal energy from low-latitude oceanic regions to polar areas through atmospheric and oceanic circulation systems. Near...
Read MoreWhy Do We have Seasons on Earth?
What Causes Earth’s Seasons? This seemingly straightforward inquiry often leads to a common misunderstanding: Although Earth follows an elliptical trajectory […]
Read MoreWhat resources are derived from marine sediments?
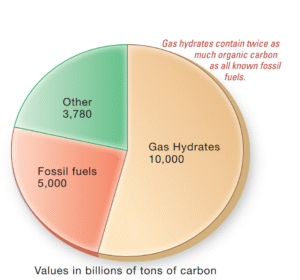
What Resources Do Marine Sediments Provide? The ocean floor harbors a wealth of potential mineral and organic assets. However, a […]
Read MoreHow Are Pelagic and Neritic Deposits Distributed?
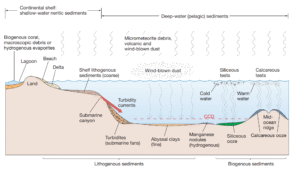
How are Pelagic and Neritic Deposits Distributed in the Ocean? Pelagic and neritic deposits are distributed based on water depth […]
Read MoreWhat Are the Characteristics of Cosmogenous Sediment?
Cosmogenous sediment (cosmos = universe, generare = to produce) originates from extraterrestrial sources. Origin, Composition, and Distribution of Cosmogenous Sediment […]
Read MoreWhat Are the Characteristics of Hydrogenous Sediment?
Hydrogenous sediment (from hydro, meaning water, and generare, meaning to produce) originates from substances that have been dissolved within aquatic […]
Read MoreWhat Are the Characteristics of Biogenous Sediment?
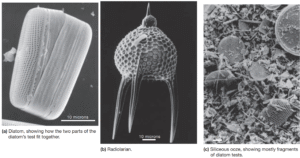
Biogenous sediment (from bio, meaning life, and generare, meaning to produce)—also known as biogenic sediment—originates from the preserved hard remains […]
Read MoreWhat Are the Characteristics of Lithogenous Sediment?
Lithogenous sediment (from lithos meaning stone and generare meaning to produce) originates from pre-existing rock formations that are found on […]
Read MoreWhat Features Exist in the Deep-Ocean Basins?
The deep-ocean region extends beyond the continental margin province—which comprises the shelf, slope, and rise—and encompasses a diverse range of […]
Read More