Latitude and Longitude
Latitude and longitude form Earth’s coordinate system for precise location mapping. Latitudes are horizontal circles (0° to 90° N/S) measuring distance from the Equator. Longitudes are vertical semicircles (0° to 180° E/W) measuring distance from the Prime Meridian at Greenwich. Key parallels include Equator (0°), Tropic of Cancer (23½°N), Tropic of Capricorn (23½°S), Arctic Circle (66½°N), and Antarctic Circle (66½°S). Every 15° longitude equals one hour time difference, making them essential for navigation, climate zones, and timekeeping worldwide.
Latitudes are horizontal circles measuring a place’s north-south distance from the Equator (0°). Longitudes are vertical semicircles gauging east-west distance from the Prime Meridian (0° through Greenwich). Together they form Earth’s coordinate grid used for navigation, time zones & climatology.
The latitudes and longitudes are essentially imaginary lines drawn on the globe to locate any place accurately. The latitudes run from east to west, parallel to the equator, while the longitudes run from north to south and pass through the poles. The location of any place on the Earth can be determined by the intersection of latitude and longitude. Both latitudes and longitudes are measured in degrees.
What Are Latitudes?

| Parameter | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
| Reference line | Equator (0°) | Prime Meridian (0°) |
| Direction | East-West circles | North-South semicircles |
| Climatic role | Heat zones | Time zones |
Latitude can be defined as an angular distance of a point on the surface of Earth from the center of the Earth. Latitudes are parallel to the equator, which lies halfway between the two poles. The latitudes become smaller towards the poles, following the shape of a sphere. The equator represents 0°, whereas the North and the South poles are at 90°N and 90°S respectively.
North of the equator, latitudes are assigned North degrees, and south of the equator, the latitudes are assigned South degrees. Between the equator and the poles, the lines or parallels of latitude are drawn at an interval of 1°. For precision of location mapping, each degree of latitude is divided into 60 minutes, and each minute into 60 seconds.
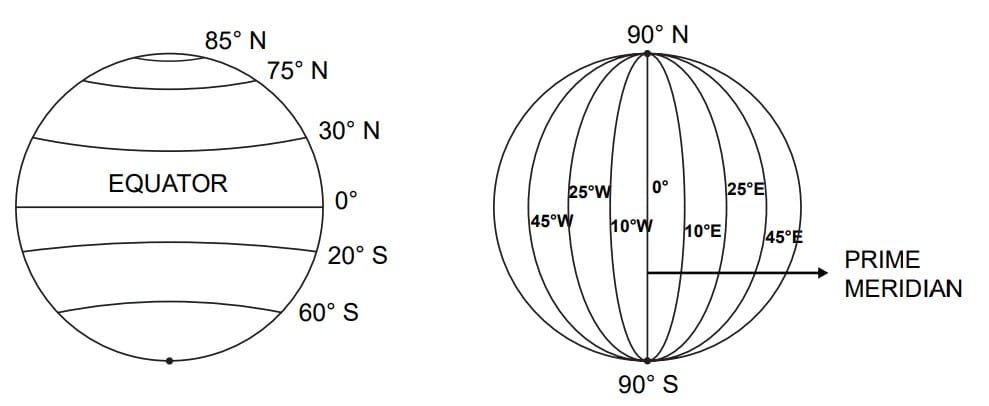
Major Parallels (Equator, Tropics, Circles)
The most important latitudes are:
- Equator at 0°
- Tropic of Cancer (23 1/2° N)
- Arctic Circle (66 1/2° N)
- Tropic of Capricorn (23 1/2° S)
- Antarctic Circle (66 1/2° S)
Because of the spherical shape of Earth, the physical distance between the latitudes increases very gradually from the equator to the poles. For example, at the equator at 0°, the distance between two latitudes is 68.704 miles. At 45°N, the difference between two latitudes is 69.054 miles, and near the pole at 90°N, it is 69.407 miles. However, for ease of purpose, the average distance between two latitudes is taken as 69 miles.
What Are Longitudes?

Longitude is the angular distance, measured in degrees, along the equator, west or east of the Prime Meridian. On the globe, longitudes are a series of semi-circles that run from north to south from one pole to the other. Each longitude cuts through the equator. Longitudes are also called Meridians.
Any longitude could have been taken as the prime meridian for the purpose of numbering. However, in 1884, by an International Agreement, it was decided that the zero meridian would pass through the Royal Astronomical Observatory at Greenwich, near London. The 0° Longitude is called the Prime Meridian, and all other meridians fall to the left or right of the prime meridian.
The longitudes are divided into 180° to the east and west of the Prime Meridian. The distance between two longitudes at the equator is calculated by dividing the circumference of the Earth by 360° (25000 miles ÷ 360 = 69.1 miles). However, the longitudes converge at the poles, so the linear distance between two longitudes narrows. For example:
- At the equator, the distance between two longitudes is 69.1 miles.
- At 45°N, it is 49 miles.
- At 75°N, it is only 18 miles.
- At the poles, it is 0 miles.
The degree of longitude thus decreases in length polewards.
Longitude & Time-Zones (with solved UPSC example)

The rotation of the Earth around the Sun means that at any point in time, different places on Earth will experience a different time of the day. Since the Earth makes one complete round of 360° in one day or 24 hours, it means that in one hour, it covers a distance of 15°, or 1° in four minutes.
As the Earth rotates from west to east, for every 15° eastwards, we gain an hour. That means the local time is advanced by an hour for every 15° eastward move. Conversely, if we go westwards, we lose an hour, meaning for every 15° westward move, the time is reduced by an hour.
Places to the east of Greenwich see sunrise earlier. A person traveling from Greenwich to the east will gain time on reaching the eastern destination compared to a person traveling to the west of Greenwich, who will lose time. The places west of Greenwich see sunrise later than sunrise in Greenwich. Generally, time is determined by the longitude of the place, compared with the local time of Greenwich, and then adjusted by adding or subtracting time depending on the longitude.
What are latitudes and longitudes?
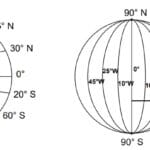
Latitudes and longitudes are imaginary lines drawn on the globe to help locate any place accurately. Latitudes run parallel to the equator (east-west), while longitudes run from pole to pole (north-south).
How are latitudes and longitudes measured?
Both latitudes and longitudes are measured in degrees. Latitudes are further divided into minutes and seconds for precise location mapping.
What is the significance of the equator in latitude?
The equator represents 0° latitude and divides the Earth into the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It serves as the starting point for measuring latitudes.
What are the most important latitudes?
The most notable latitudes are:
Equator (0°)
Tropic of Cancer (23 1/2° N)
Arctic Circle (66 1/2° N)
Tropic of Capricorn (23 1/2° S)
Antarctic Circle (66 1/2° S)
What is the Prime Meridian in longitude?
The Prime Meridian is the 0° longitude line that passes through the Royal Astronomical Observatory at Greenwich, London. It divides the Earth into the Eastern and Western Hemispheres.
How do longitudes affect time?
Since the Earth rotates 360° in 24 hours, each 15° of longitude corresponds to a time difference of one hour. Moving eastward adds time, while moving westward subtracts time.
Why do distances between longitudes vary?
The distances between longitudes decrease as they approach the poles due to the convergence of the meridians. For example, the distance between two longitudes is 69.1 miles at the equator but narrows to zero at the poles.
What are the uses of latitude and longitude?
Latitudes and longitudes are crucial for navigation, mapping, and determining the location of any point on Earth. They also help in time calculation based on longitude.
What is the importance of the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn?
The Tropic of Cancer (23 1/2° N) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23 1/2° S) mark the farthest points north and south where the sun can appear directly overhead.
How do we calculate time using longitudes?
Time is calculated by comparing the longitude of a location with the Prime Meridian. For every 15° eastward, one hour is added, and for every 15° westward, one hour is subtracted.
What is the distance between two latitudes?
The average distance between two latitudes is approximately 69 miles. However, this varies slightly due to the Earth’s spherical shape.
How are latitudes and longitudes used in mapping?
Latitudes and longitudes create a grid system on the globe, allowing for precise mapping and location identification, which is essential for cartography and navigation.
Why is the distance between latitudes consistent?
The distance between latitudes remains consistent because they are parallel to each other, unlike longitudes, which converge at the poles.
What role do latitudes play in climate zones?
Latitudes are key in determining climate zones. For example, regions near the equator experience a tropical climate, while those near the poles experience a polar climate.
Why was Greenwich chosen as the Prime Meridian?
Greenwich was chosen as the Prime Meridian during an international agreement in 1884 because of its significance in navigation and its use by many countries for map-making and timekeeping.
