Standard Time and Time Zones – Physical Geography (UPSC)
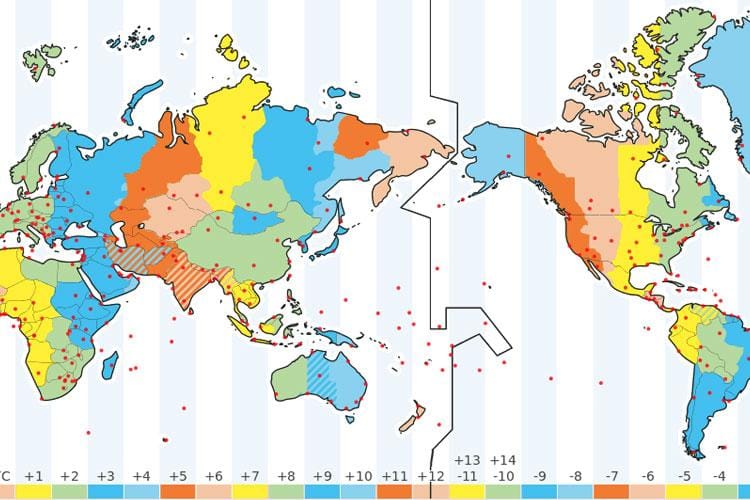
Standard Time and Its Necessity Now for each city or a place to keep individual time based on its longitudinal position would complicate matters, especially in cases of medium to big countries. Since for each degree change in longitude, there is a time difference of four minutes, people travelling from one part to other part […]
Standard Time and Time Zones – Physical Geography (UPSC) Read More »