Exam Pattern: EARTH, ATMOSPHERIC, OCEAN AND PLANETARY SCIENCES
| | PART A | PART B | PART C | TOTAL |
|---|
| Total questions | 20 | 50 | 80 | 150 |
| Max No. of Questions to attempt | 15 | 35 | 25 | 75 |
| Marks for each correct answer | 2 | 2 | 4 | 200 |
| Marks for each incorrect answer (Negative marking for part A & B is @ 25%, and part C is @ 33%) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.32 | – |
The candidate is required to answer a maximum of 15, 35, and 25 questions from Part-A, Part-B, and Part-C, respectively. If more than the required number of questions are answered, only the first 15, 35, and 25 questions in Part A, Part B, and Part C, respectively, will be taken up for evaluation.
Below each question in Part A, Part B, and Part C, four alternatives or responses are given. Only one of these alternatives is the “correct” option to the question. The candidate has to find, for each question, the correct or the best answer.
Syllabus
EARTH, ATMOSPHERIC, OCEAN AND PLANETARY SCIENCES
PAPER I (PART B)
The Earth and the Solar System
- Milky Way and the solar system.
- Modern theories on the origin of the Earth and planetary bodies.
- Earth’s orbital parameters, Kepler’s laws of planetary motion.
- Geological Time Scale; space and time scales of processes in the solid Earth, atmosphere, and oceans.
- Radioactive isotopes and their applications.
- Meteorites: chemical composition and primary differentiation of the Earth.
- Basic principles of stratigraphy.
- Theories about the origin of life and fossil records.
- Earth’s gravity, magnetic fields, and thermal structure: Geoid and spheroid concepts; Isostasy.
Earth Materials, Surface Features, and Processes
- Gross composition and physical properties of important minerals and rocks.
- Properties and processes responsible for mineral concentrations.
- Distribution of rocks and minerals in Earth’s units and India.
- Physiography of the Earth; weathering, erosion, and soil formation.
- Energy balance of Earth’s surface processes.
- Physiographic features and river basins in India.
Interior of the Earth, Deformation, and Tectonics
- Basic concepts of seismology and Earth’s internal structure.
- Physico-chemical and seismic properties of Earth’s interior.
- Stress and strain concepts; rock deformation.
- Folds, joints, and faults; causes and measurement of earthquakes.
- Interplate and intraplate seismicity; paleomagnetism.
- Sea-floor spreading and plate tectonics.
Oceans and Atmosphere
- Hypsography of continents and ocean floors: continental shelves, slopes, abyssal plains.
- Physical and chemical properties of seawater; residence times of elements.
- Ocean currents, waves, tides, thermohaline circulation, and conveyor belts.
- Major water masses, biological productivity, and fluid motion.
- Atmospheric structure and heat budget; greenhouse gases and global warming.
- General circulation, monsoon systems, ENSO, cyclones, and local systems in India.
- Marine and atmospheric pollution, ozone depletion.
Environmental Earth Sciences
- Properties of water and the hydrological cycle.
- Energy resources: uses, degradation, alternatives, and management.
- Ecology, biodiversity, and natural resource conservation.
- Natural hazards and remote sensing applications.
PAPER I (PART C)
I. Geology
Mineralogy and Petrology
- Point group, space group, and lattice concepts.
- Crystal field theory, mineralogical spectroscopy, and bonding in mineral structures.
- Genesis, properties, and crystallization of magmas.
- Metamorphic structures, textures, and thermobarometry.
- Petrogenesis of Indian rock suites: Deccan Traps, charnockites, ophiolites, and more.
Structural Geology and Geotectonics
- Stress and strain analysis; Mohr circles.
- Geometry and mechanics of folds, faults, and ductile shear zones.
- Plate boundaries, mantle plumes, and Himalayan orogeny.
Paleontology and Applications
- Life origin theories, evolution models, and mass extinctions.
- Applications of fossils in age determination, paleoecology, and paleogeography.
- Micropaleontology in hydrocarbon exploration.
Sedimentology and Stratigraphy
- Classification of sediments and sedimentary rocks.
- Sedimentary environments and basin evolution.
- Stratigraphic principles, correlation methods, and sequence stratigraphy.
- Phanerozoic stratigraphy of India.
Marine Geology and Paleoceanography
- Ocean floor morphology, ocean circulation, and thermohaline processes.
- Factors influencing oceanic sediments and paleoceanographic reconstruction.
Geochemistry
- Atomic properties, periodic table, thermodynamics of reactions, and isotopes in geochronology.
- Applications of stable isotopes in Earth processes.
Economic Geology
- Ore formation processes, mineral deposit studies, and petroleum geology.
- Coal and unconventional energy resources.
Precambrian Geology and Crustal Evolution
- Evolution of Earth systems and Precambrian characteristics of India.
- Precambrian–Cambrian boundary.
Quaternary Geology
- Quaternary stratigraphy, climate variability, and human evolution.
- Dating methods and tectonic geomorphology.
Applied Geology
- Remote sensing and GIS.
- Engineering properties of rocks; construction investigations.
- Methods of mineral exploration and groundwater studies.
II. Physical Geography
- Geomorphology: Landform processes, DEM analysis, extraterrestrial geomorphology.
- Climatology: Radiation balance, wind systems, ENSO, and climate classification.
- Biogeography: Plant and animal associations, Indian biogeography, and conservation.
- Environmental Geography: Man-land relationships, hazards, and ecological balance.
- Geography of India: Physical geography, climatology, agriculture, and population characteristics.
III. Geophysics
- Signal Processing: Fourier transforms, filters, and signal analysis.
- Field Theory: Newtonian potential, Green’s theorem, and seismic wave propagation.
- Numerical Analysis and Inversion: Least squares, optimization, and pattern recognition.
- Gravity and Magnetic Methods: Data interpretation and anomaly analysis.
- Seismic Methods: Ray theory, reflection/refraction techniques, seismic stratigraphy.
- Well Logging: Techniques for lithology, porosity, and fluid saturation interpretation.
(IV) METEOROLOGY
1) Climatology
2) Physical Meteorology
- Thermal Structure of the Atmosphere and Its Composition.
- Radiation:
- Basic laws – Rayleigh and Mie scattering, multiple scattering.
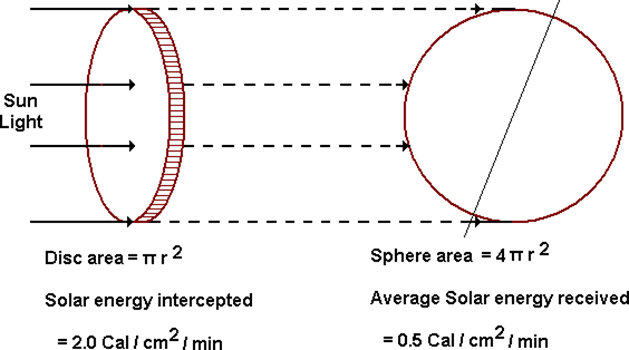
- Radiation from the sun, solar constant, effect of clouds, surface and planetary albedo.
- Emission and absorption of terrestrial radiation, radiation windows, radiative transfer, Greenhouse effect, net radiation budget.
- Thermodynamics of Dry and Moist Air:
- Specific gas constant, adiabatic and isentropic processes, entropy and enthalpy.
- Moisture variables, virtual temperature, Clausius–Clapeyron equation.
- Adiabatic processes of moist air, thermodynamic diagrams.
- Hydrostatic Equilibrium:
- Hydrostatic equation, variation of pressure with height, geopotential, standard atmosphere, altimetry.
- Vertical Stability of the Atmosphere:
- Dry and moist air parcel and slice methods, tropical convection.
- Atmospheric Optics:
- Visibility and optical phenomena – rainbows, haloes, corona, mirage, etc.
3) Atmospheric Electricity
- Fair weather electric field in the atmosphere and potential gradients.
- Ionization in the atmosphere, electrical fields in thunderstorms.
- Theories of thunderstorm electrification, structure of lightning flash, mechanisms of earth-atmospheric charge balance, and the role of thunderstorms.
4) Cloud Physics
- Cloud classification, condensation nuclei, growth of cloud drops and ice-crystals.
- Precipitation mechanisms: Bergeron–Findeisen process, coalescence process.
- Precipitation of warm and mixed clouds, artificial precipitation, hail suppression, fog and cloud dissipation.
- Radar observation of clouds and precipitation:
- Radar equation, rain drop spectra, radar echoes of hailstorms, tornadoes, hurricanes, and rainfall measurements.
5) Dynamic Meteorology
- Basic Equations and Fundamental Forces:
- Pressure, gravity, centripetal and Coriolis forces.
- Continuity and momentum equations (Cartesian and spherical coordinates).
- Scale analysis, inertial flow, geostrophic and gradient winds, thermal wind.
- Divergence and vertical motion, Rossby, Richardson, Reynolds, and Froude numbers.
- Atmospheric Turbulence:
- Mixing length theory, planetary boundary layer equations, Ekman layer, eddy transport of heat, moisture, and momentum.
- Linear Perturbation Theory:
- Internal and external gravity waves, inertia waves, gravity waves, Rossby waves, wave motion in the tropics, barotropic and baroclinic instabilities.
- Atmospheric Energetics:
- Kinetic, potential, and internal energies; conversion into kinetic energy; available potential energy.
6) Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP)
- Computational instability, filtering of sound and gravity waves.
- Filtered forecast equations, barotropic and baroclinic models.
- Objective analysis, data assimilation techniques, satellite applications in NWP.
7) General Circulation and Climate Modelling
- Observed zonally symmetric circulations, meridional circulation models.
- General circulation modelling principles: grid-point and spectral GCMs.
- Climate variability phenomena: ENSO, QBO, MJO, etc.
- Ocean-atmosphere coupled models.
8) Synoptic Meteorology
- Weather observations and transmission, synoptic charts.
- Synoptic weather forecasting, prediction of weather elements, and hazardous weather phenomena.
- Tropical Meteorology:
- ITCZ, monsoons, tropical cyclones, jet streams.
- Extra-Tropical Features:
- Jet streams, extratropical cyclones, anticyclones.
- Air masses and fronts: sources, classification, frontogenesis, and associated weather.
9) Aviation Meteorology
- Meteorological role in aviation, weather hazards during takeoff, cruising, and landing.
- In-flight hazards: icing, turbulence, visibility issues, gusts, wind shear, thunderstorms.
10) Satellite Meteorology
- Polar orbiting and geostationary satellites.
- Applications in identifying synoptic systems, cyclones, temperature estimation, rainfall prediction, and temperature/humidity soundings.
(V) OCEAN SCIENCES
1) Physical Oceanography
- T-S diagrams, mixing processes, characteristics of water masses.
- Wind-generated waves, shallow and deep-water wave dynamics.
- Coastal processes: wave reflection, refraction, diffraction, littoral currents, rip currents, tsunami, and more.
- Ocean Circulation:
- Global conveyor belt circulation, Ekman’s theory, upwelling processes.
2) Chemical Oceanography
- Composition of seawater, chemical exchanges, and classification of elements.
- Element chemistry under special conditions (estuaries, vents, etc.).
- Carbonate chemistry, biological pumps, and sedimentary deposit factors.
3) Geological Oceanography
- Topics as listed under “Marine Geology & Paleoceanography.”
4) Biological Oceanography
- Classification of marine environments and organisms.
- Primary and secondary production, factors affecting biodiversity.
- Human impacts on marine communities and climate change effects.
How Study Hub Can Help You Prepare for the Earth, Atmospheric, Ocean, and Planetary Sciences Syllabus
Preparing for the extensive and demanding syllabus of Earth, Atmospheric, Ocean, and Planetary Sciences (702) requires a strategic approach and access to comprehensive study resources. Study Hub (accessible at studyhub.net.in) offers unparalleled support to help candidates excel in this challenging domain. Here’s how Study Hub can guide your preparation:
Comprehensive Coverage of Topics
At Study Hub, we provide in-depth study materials, mock tests, and curated articles to help candidates grasp even the most complex topics. Our resources are designed to address every aspect of the syllabus, including:
Meteorology: Understand critical concepts like the thermal structure of the atmosphere, radiative transfer, vertical stability, numerical weather prediction, general circulation and climate modelling, and the role of satellite meteorology in observing weather systems such as cyclones, monsoons, and thunderstorms.
Ocean Sciences: Dive into topics such as physical oceanography, chemical oceanography, geological oceanography, and biological oceanography. Study Hub’s resources emphasize key aspects like upwelling processes, estuarine circulation, ocean eddies, Ekman theory, and global conveyor belt circulation—helping you understand the intricate processes of ocean systems.
Atmospheric Dynamics and Energetics: Through articles, conceptual guides, and practice questions, candidates gain a strong grasp of fundamental equations, vorticity, geostrophic winds, Rossby waves, atmospheric turbulence, and barotropic and baroclinic instabilities.
Planetary Sciences: Our expertly crafted content helps students explore planetary structures, processes, and phenomena with precision, complementing other topics under Earth Sciences for an interdisciplinary understanding.
Mock Tests and Evaluation Framework
We align our mock tests and sample papers with the pattern of the Earth Sciences examination:
- Objective Analysis for Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP): Test your knowledge of filtered forecasting models and data assimilation techniques.
- Synoptic Meteorology Practices: Work on real-world weather data and forecast exercises involving tropical cyclones, ITCZ systems, monsoon depressions, and jet streams.
- Topic-specific tests ensure mastery in areas like atmospheric optics, biochemical nutrient cycling, and the impact of human activities on ecosystems.
Why Study Hub is the Perfect Partner for Your Earth Sciences Preparation
- Academic Rigor: Study Hub maintains an academic tone throughout its resources, ensuring in-depth coverage of essential keywords such as radiative budget, MJO (Madden-Julian Oscillation), Quasi-Biennial Oscillation (QBO), and ENSO phenomena.
- Focused on Practical Applications: Be it radar observations, wave refraction techniques, or the impact of anthropogenic inputs on marine biodiversity, we emphasize the practical relevance of each topic for better comprehension.
- Adaptive Materials: From simple T-S diagrams to advanced topics like geopotential variation and numerical baroclinic models, we tailor our resources to match both beginner and advanced levels of understanding.