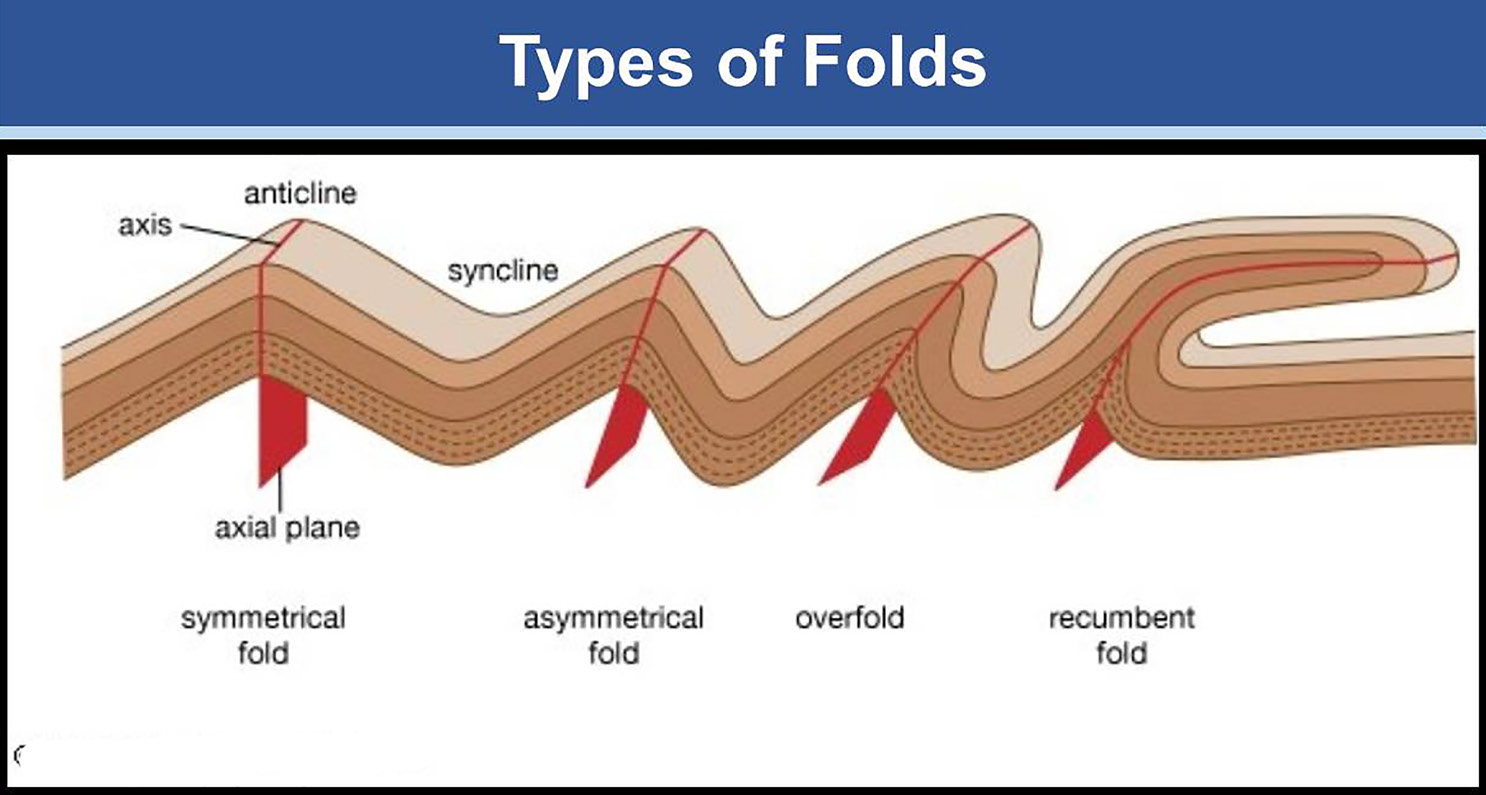
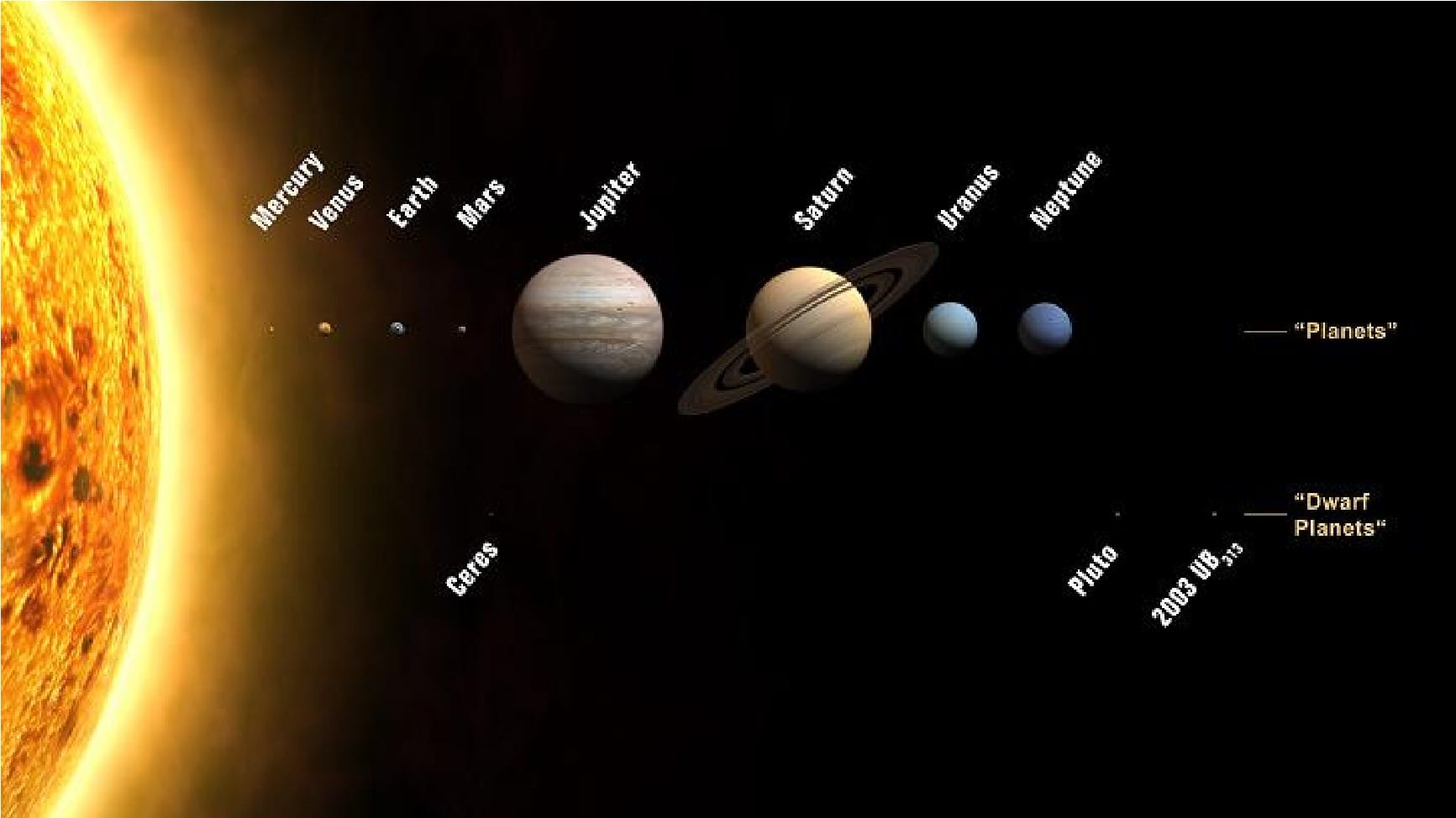
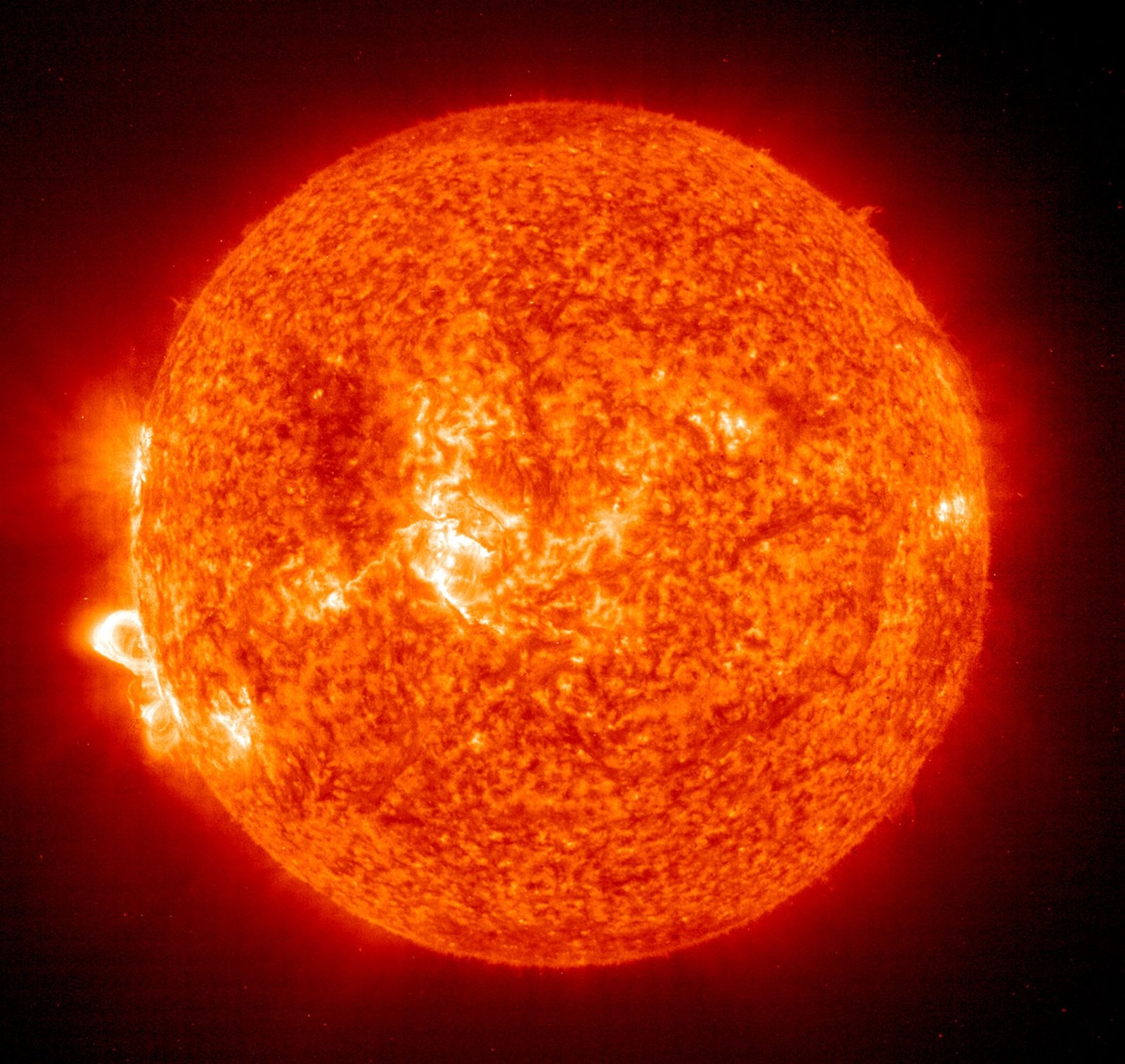
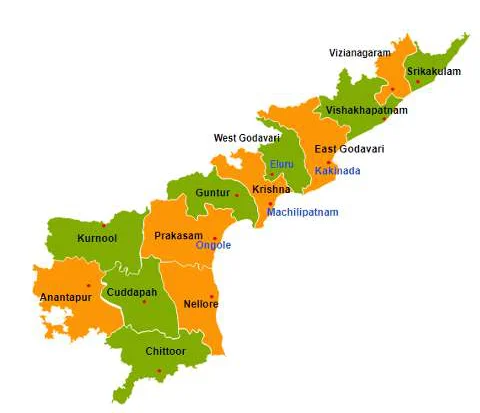
विद्या ददाति विनयं विनयाद्याति पात्रताम्। पात्रत्वाद्धनमाप्नोति धनाद्धर्मं ततः सुखम्॥
Knowledge brings humility; from humility comes worthiness; with worthiness comes wealth and with wealth one performs duties; in performing duties, one becomes happy.
Never miss a headline!
Subscribe to our newsletter for daily updates.
Get the latest stories delivered straight to your inbox.
StudyHUB – Free Open Educational Resources
Your complete guide for competitive exam preparation.
Welcome to StudyHUB
At StudyHUB, we strive to provide students and job aspirants with comprehensive study materials and tools to achieve their goals. Our resources cover a wide range of subjects, including History, Polity, Geography, MP GK, India GK, and much more. We also offer current affairs updates, quizzes, and valuable courses designed to cater to competitive exams at all levels.
We are now providing completely free PYQs and MCQs quizzes for all exams in both Hindi and English.
What is StudyHUB?
StudyHUB is a one-stop platform for aspirants preparing for competitive exams like:
- UPSC (Union Public Service Commission)
- MPPSC (Madhya Pradesh Public Service Commission)
- RPSC (Rajasthan Public Service Commission)
- UPPSC (Uttar Pradesh Public Service Commission)
- State PSC Exams across India
- Banking Exams (IBPS, SBI PO/Clerk, RBI Exams)
- GATE (Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering)
- SSC Exams (Staff Selection Commission)
- Many more national and state-level examinations.
Why Choose StudyHUB?
Comprehensive Study Material
We provide high-quality study notes and PDFs for all subjects, tailored to specific exams.
Regular Current Affairs Updates
Stay updated with daily, weekly, and monthly current affairs, crucial for exams like UPSC, State PSC, and Banking.
Engaging Quizzes
Test your knowledge with topic-wise quizzes and full-length mock tests to enhance your preparation.
Job Notifications
Never miss an opportunity with our timely updates on government and private job openings.
Expert Tips and Guidance
Get valuable tips and strategies to crack exams from experienced mentors.
Our Features
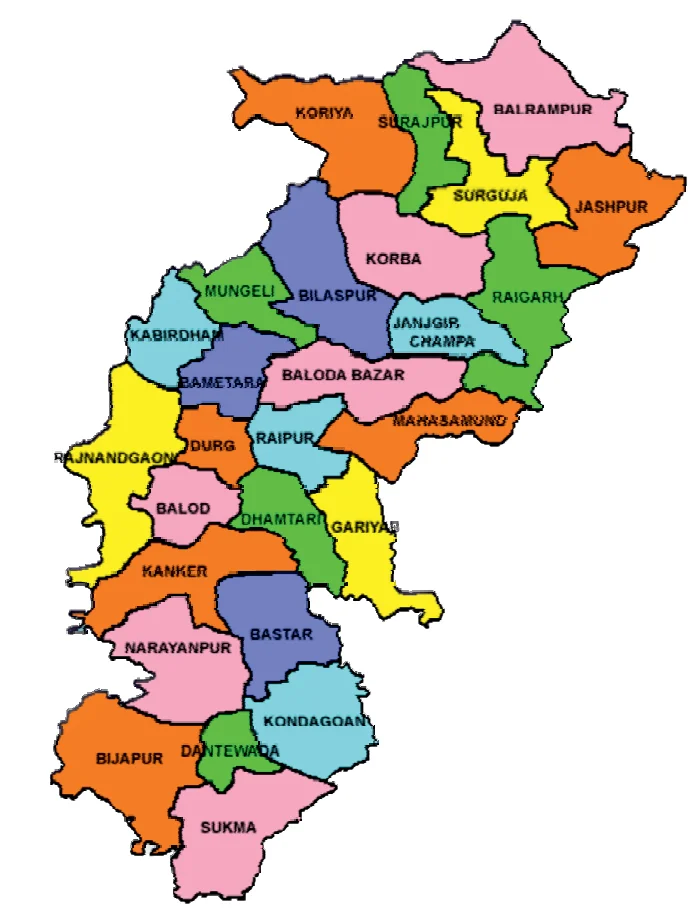
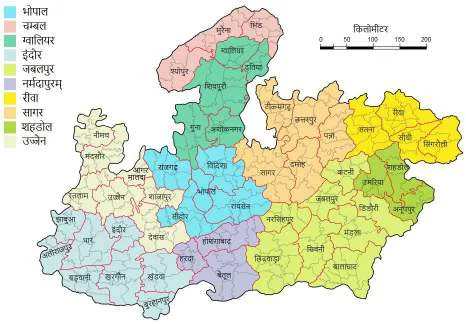
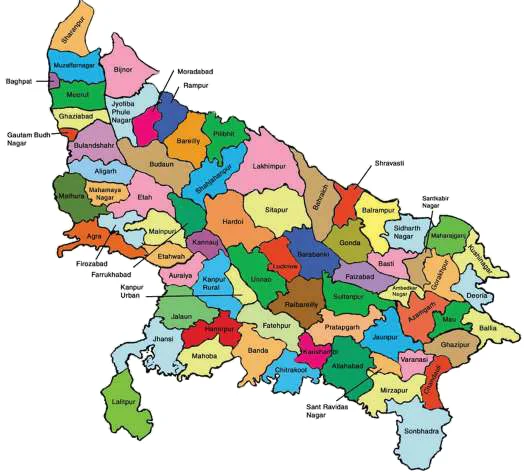
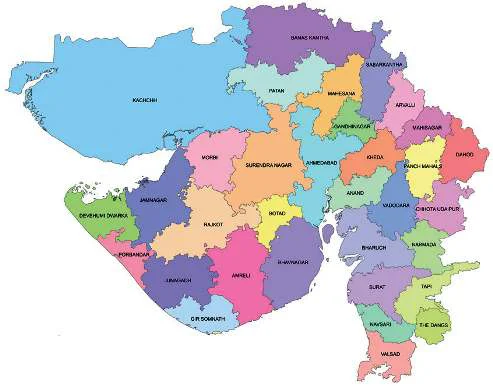
- Subject-Wise Resources: Dedicated materials for History, Geography, Polity, MP GK, India GK, and more.
- Custom Quizzes: Practice with quizzes designed to match exam patterns.
- GATE Resources: Specially curated content for GATE aspirants.
- Exam Preparation Tips: Strategies to manage time, solve questions effectively, and improve accuracy.
- Job Alerts: Real-time updates on government and private job vacancies.
Study Tips for Aspirants
- Stay Organized: Create a timetable and stick to it.
- Revise Regularly: Go through notes and quizzes multiple times to retain information.
- Practice Mock Tests: Attempt mock tests to simulate the real exam experience.
- Stay Updated: Follow our current affairs section for the latest news and events.
- Ask for Help: Join our community to discuss doubts and seek guidance from experts.
How to Get Started?
- Explore our website for study materials, current affairs, and quizzes.
- Take quizzes and download PDFs to boost your preparation.
- Contact us for guidance and tips from our experienced mentors.
Contact Us
Have questions or need assistance? We’re here to help! Reach out to us anytime through our contact page on the website.